Carbohydrates often get a bad rap in the world of nutrition, but they are essential for providing the energy our bodies need to function. Not all carbs are created equal, though. Understanding the differences between simple and complex carbs, as well as the role of fiber, can help you make healthier choices. In this blog, we’ll break down everything you need to know about healthy carbs.
Simple vs. Complex Carbs
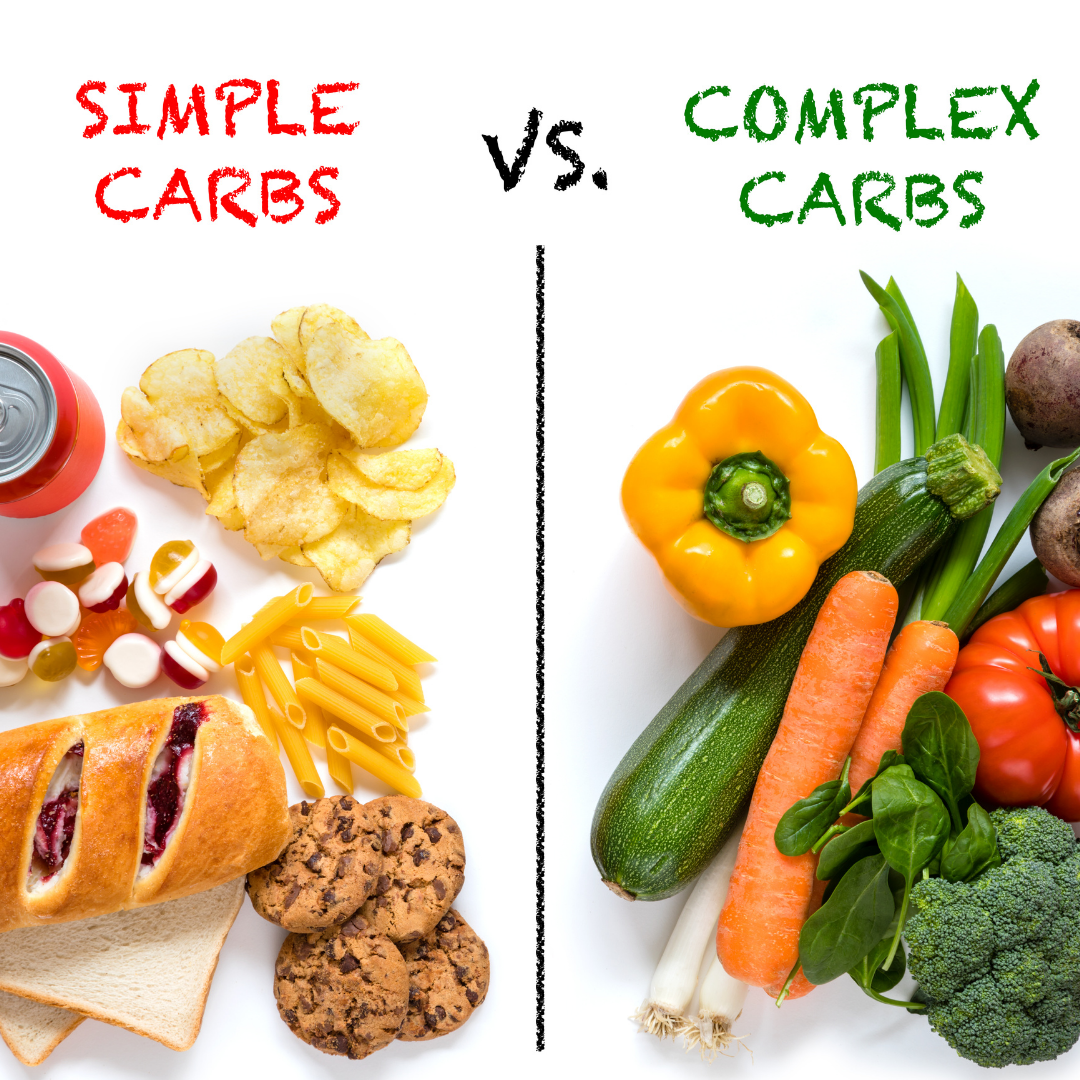
Carbohydrates are categorized into two main types: simple and complex.
Simple Carbs
Simple carbs are composed of one or two sugar molecules and are quickly digested and absorbed by the body. They provide a rapid source of energy but can lead to blood sugar spikes.
- Sources: Sugary snacks, candies, fruits, and some dairy products.
- Fact: Simple carbs are found in both natural sources (like fruit) and processed foods (like candy).
Complex Carbs
Complex carbs consist of long chains of sugar molecules, which take longer to break down and provide a more sustained energy release.
- Sources: Whole grains, legumes, vegetables, and starchy foods like potatoes.
- Fact: Complex carbs are rich in fiber, vitamins, and minerals, making them a healthier choice compared to simple carbs.
Fast vs. Slow Digesting Carbs
Another way to classify carbs is by their digestion rate—fast or slow.
Fast Digesting Carbs
These carbs are rapidly absorbed, causing a quick increase in blood sugar levels. They are useful for immediate energy needs but can lead to energy crashes.
- Sources: White bread, sugary cereals, and certain processed foods.
- Fact: Fast digesting carbs are often high in simple sugars and low in fiber.
Slow Digesting Carbs
Slow digesting carbs release glucose gradually into the bloodstream, providing a steady source of energy and helping to maintain stable blood sugar levels.
- Sources: Oats, brown rice, quinoa, and most vegetables.
- Fact: Slow digesting carbs are typically rich in fiber, which slows down the digestion process.
The Role of Fiber
Fiber is a type of carbohydrate that the body cannot digest. It plays a crucial role in maintaining digestive health and regulating blood sugar levels. Fiber is divided into two main types: soluble and insoluble.
Soluble Fiber
Soluble fiber dissolves in water to form a gel-like substance, which can help lower blood cholesterol and glucose levels.
- Sources: Oats, apples, citrus fruits, and legumes.
- Fact: Soluble fiber can help slow down digestion, making you feel fuller for longer.
Insoluble Fiber
Insoluble fiber does not dissolve in water and helps add bulk to the stool, promoting regular bowel movements.
- Sources: Whole grains, nuts, beans, and vegetables like carrots and celery.
- Fact: Insoluble fiber aids in preventing constipation and maintaining a healthy digestive system.
How to Incorporate Healthy Carbs into Your Diet
- Choose Whole Grains: Opt for whole grains like brown rice, quinoa, and whole wheat bread over refined grains.
- Eat More Fruits and Vegetables: These are natural sources of healthy carbs and are packed with vitamins, minerals, and fiber.
- Limit Sugary Snacks: Reduce your intake of processed foods and sugary snacks to avoid blood sugar spikes and crashes.
- Balance Your Plate: Include a variety of carbs in your meals, focusing on complex carbs and high-fiber foods to maintain steady energy levels throughout the day.
Conclusion
Understanding the different types of carbohydrates and their roles can help you make better nutritional choices. By focusing on complex, slow-digesting carbs and incorporating plenty of fiber into your diet, you can enjoy steady energy levels and better overall health. Remember, carbs are not the enemy—it’s all about choosing the right ones. Need personalized guidance on your nutrition journey? Reach out today for a free discovery session or message me on Instagram and let’s explore how we can help you achieve your health goals!